VMU development: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
=== Community === | === Community === | ||
If you | If you have any questions, want to share your work, would like to contribute in any way, or would like to hang out with a community of other people interested in VMU and Dreamcast development, try the following links: | ||
* [http://dcemulation.org/phpBB/ DCEmu Forums] - One of the biggest, most prolific Dreamcast web forums, with a technical goldmine of information | * [http://dcemulation.org/phpBB/ DCEmu Forums] - One of the biggest, most prolific Dreamcast web forums, with a technical goldmine of information | ||
* [http://dreamcast-talk.com/forum/index.php Dreamcast-Talk Forums] - A popular Dreamcast gaming and homebrew enthusiast forum | * [http://dreamcast-talk.com/forum/index.php Dreamcast-Talk Forums] - A popular Dreamcast gaming and homebrew enthusiast forum | ||
Revision as of 14:18, 29 December 2022
Developing standalone games for the Sega Dreamcast's VMU (also known as VMS) is both a challenging and rewarding development feat. On one hand, it's not the easiest embedded device to target, given that it doesn't have a C compiler and has its own set of hardware eccentricities. On the other hand, the device features a rich instruction set, 3 different clock sources, a FAT filesystem, and many different peripherals which can be leveraged by a developer, making it something of a Sega Saturn of little 8-bit gaming devices.
While there is an active and ongoing effort within the scene to lower the barrier of entry into VMU development and to get more high-quality tutorials and materials out there for newbies, this page will hopefully serve as an entry point based on what is currently available.
Hardware
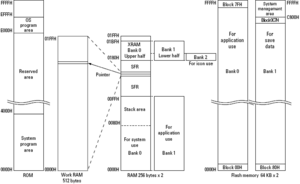
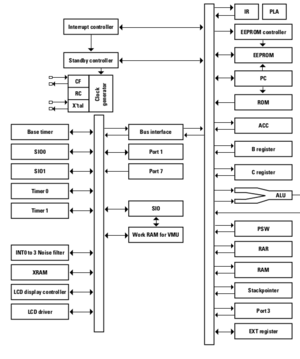
A high-level overview of the VMU's technical specifications can be found here. A good initial look at application-development for the device can be found at Marcus Comstedt's VMU Programming Site. A combination of this site and the official VMU Development Manual is typically what is referenced while programming for the VMU. Between the two, a developer should have all of the hardware documentation necessary to cover the following concepts:
- Address Spaces, memory segments and banks
- Opcodes and instructions
- Addressing modes
- System vs application execution
- Built-in firmware routines
- Special Function Registers (SFRs)
- Interrupt service routines and their configuration
- Controlling clock and oscillator circuits
- Driving the LCD display by writing to XRAM
- Reading/Writing to extra Working Memory (WRAM)
- Controlling the Base Timer, and 2 Timer/Counter peripherals
- Driving the piezoelectric Buzzer for sound output
- Detecting button presses on Port 3
- Serial communications via the 2 SIO interfaces
Programming
Since there is no C compiler for the VMU's 8-bit Sanyo CPU, development is traditionally done in Sanyo LC86k assembly language; however, it is now possible to write C code indirectly targeting the device via emulation of the ARM Cortex M23 CPU.
LC86k Assembly Code
The Waterbear assembler/disassembler is the favored tool for creating VMU binaries, as it is cross-platform, is feature-rich, supports all undocumented opcodes and SFRs, and is still under active development. You can find it here.
LibPerspective
Due to the non-contiguous, banked nature of XRAM, it is actually a nontrivial engineering feat to blit an image to the LCD screen. LibPerspective is a simple rendering library developed to aid in such tasks. It is frequently used in modern VMU homebrew and will enable you to work with rendering bitmaps to the display much more quickly. More information can be found here.
VMS Tetris
The source code to Marcus Comstedt's VMU version of Tetris serves as a a great beginner resource, as it is well-commented and is a fairly complex game. The source code can be found here.
Raining Squares
Raining Squares is a tech demo which serves as a great example for newbies to the platform. More information can be found here.
C Code
Thanks to the uM23 emulator, it is now possible to indirectly write C code for the VMU. The code is cross-compiled for the ARM Cortex M23 target, and the resulting binary image is then loaded onto the VMU as a "DATA" file. The uM23 emulator, which must be loaded onto the device as the main "GAME" file, will then allow you to select an ARM binary image to run from its menu. More information can be found here.
VMU Script
A long-lost and forgotten VMU-specific pseudo scripting language which was around at the time of the Dreamcast's commercial lifespan and was used in at least one shipping commercial game. Unfortunately the language and tools have been lost to time.
VMU Animator
While not technically code or a programming language, the VMU Animator tool allowed for the easy creation of VMU animations or movies. These animations could then be exported to a VMS GAME file which could then be played on the actual device. Many of these animations are circulating around today, and the Booyaka website was an entire community based around them. Unfortunately the tool is rather dated and may not run under modern Windows. It can be found here: File:VMU Animator.zip. Note that the ElysianVMU emulator can play the intermediate .LCD files but cannot create or modify them.
Testing
Emulators
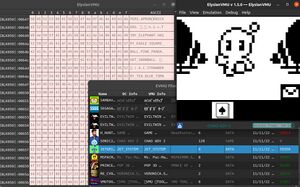
The favored emulator for VMU development and testing is the ElysianVMU emulator, as it is cross-platform, is ranked top for features and accuracy, and is still actively developed. The emulator also has an explicit goal of offering a debugging environment to facilitate development. Much of the debugger is still under active development; however, just features like the RAM and flash memory explorer widgets can be of great use during development. More information can be found here.
Physical Device
Before publishing or distributing your game, it is highly recommended that you still test on physical hardware. There are various ways through which one can get a GAME file onto the actual device depending on your Dreamcast's configuration and peripherals.
- VMU Tool
- DreamShell
- Web Browser
- Nexus Memory Card
Tips and Tricks
Grayscale Graphics
Several VMU games emulate grayscale graphics by alternating a pixel between black and white, where the resulting shade of gray that is produced is a function of the alternation frequency. This is possible due to the physical hardware characteristics of the LCD screen, as a pixel is not instantaneously lit, but rather has a small "fade-in" period. The ElysianVMU emulator attempts to emulate this behavior with the "pixel ghosting" option.
Unconstrained Flash Access
While the BIOS-provided flash operations constrain reads and writes to within the boundaries of the GAME file, it is possible to write and read directly to and from flash using the STF and LDF undocumented VMU instructions (supported by Waterbear) respectively. These instructions are what the BIOS uses to implement the higher-level firmware calls. Several homebrew games and applications have leveraged these to access other files stored within the VMU. One example is Dmitry's uM23 emulator using LDF to read ARM binaries as separate "DATA" files on the same filesystem.
USB-Powered VMU Mod
If you're constantly finding yourself in need of replacement CR2032 batteries during development, consider doing the USB Powered VMU Hack on a spare VMU.
Community
If you have any questions, want to share your work, would like to contribute in any way, or would like to hang out with a community of other people interested in VMU and Dreamcast development, try the following links:
- DCEmu Forums - One of the biggest, most prolific Dreamcast web forums, with a technical goldmine of information
- Dreamcast-Talk Forums - A popular Dreamcast gaming and homebrew enthusiast forum
- Simulant Discord - The main hangout spot for Dreamcast developers within the scene
- Elysian Shadows Discord - A smaller hangout for DC developers with many VMU-focused developers, including the authors of WaterBear, ElysianVMU, and uM23
References
- Marcus Comstedt's VMU Programming Site - Architecture overview, instruction map, SFR references, etc
- Dmitry.gr VMU hacking - uM23 Emulator Homepage
- Slum Online development - LibPerspective and other VMU content
- ElysianVMU - Emulator, File Manager, Debugger
- Waterbear - VMU Assembler, Disassembler, VMS tools
- VMU Development and Tools - Largely outdated with many broken links, still useful as a reference
- VMU Dev - Archived VMU Development site with assorted old, but useful information
- VMU.pdf - Official Sega VMU Development Manual