VMU serial communication: Difference between revisions
(Created page with " 600x600px|left|VMU Connector Pin-Out {| class="wikitable" |- ! Pin !! Function |- | 2 || CLKi |- | 3 || RX |- | 4 || TX |- | ... || ... |-...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The VMU incorporates a 2-channel synchronous serial interface with data word length of 8-bits. When plugged into the controller, this peripheral is responsible for driving the [[VMU_peripheral|Maple Communication]], enabling the VMU to act as a slave device to the Dreamcast. When plugged into each other, these peripherals allow two standalone VMUs to communicate with one-another. The 2 channels of the peripheral are referred to as SIO0 and SIO1 in the official documentation: [[File:VMU.pdf|Official Documentation]]. | |||
[[File:VMU Connector Pin-Out.jpg|600x600px | Features: | ||
* 2-channel synchronous serial interface | |||
* selectible transfer clock | |||
* SIO0 hasa transfer clock with switchable polarity | |||
* LSB/MSB switchable start sequence | |||
* switchable operation modes | |||
* overrun detection | |||
* transfer bit length control | |||
== VMU-to-Dreamcast Communications == | |||
Coming Soon... | |||
== VMU-to-VMU Communications == | |||
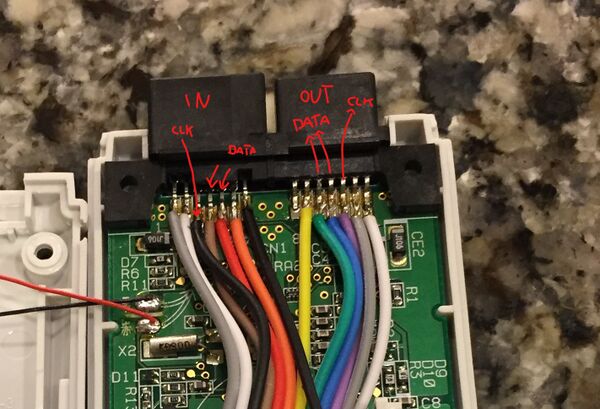
[[File:Dreamcast-VMUs-Hooked.jpg|thumb|VMU-to-VMU Connectivity]] | |||
The VMU also supports connecting to other VMU devices. This allows the the user to transfer files within the file manager of the system BIOS and exchange data within certain VMU games such as Chao Adventure. | |||
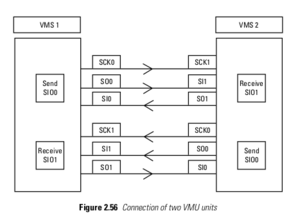
[[File:VMU-to-VMU Serial.png|thumb|VMU-to-VMU Serial Configuration]] | |||
[[File:VMU Connector Pin-Out.jpg|600x600px|VMU Connector Pin-Out]] | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Pin !! Function | ! Pin !! Function !! Name | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2 || CLKi | | 2 || CLKi || SCK1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || RX | | 3 || RX || SI1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4 || TX | | 4 || TX || SO1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| ... || ... | | ... || ... || ... | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 10 || TX | | 10 || TX || SO0 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 11 || RX | | 11 || RX || SI0 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 13 || CLKo | | 13 || CLKo || SCK0 | ||
|} | |} | ||
NOTE: During VMU-to-VMU file transfers, driven by the BIOS, RX is 1 byte delayed "echo" of TX. | |||
Latest revision as of 08:35, 25 March 2023
The VMU incorporates a 2-channel synchronous serial interface with data word length of 8-bits. When plugged into the controller, this peripheral is responsible for driving the Maple Communication, enabling the VMU to act as a slave device to the Dreamcast. When plugged into each other, these peripherals allow two standalone VMUs to communicate with one-another. The 2 channels of the peripheral are referred to as SIO0 and SIO1 in the official documentation: File:VMU.pdf.
Features:
- 2-channel synchronous serial interface
- selectible transfer clock
- SIO0 hasa transfer clock with switchable polarity
- LSB/MSB switchable start sequence
- switchable operation modes
- overrun detection
- transfer bit length control
VMU-to-Dreamcast Communications
Coming Soon...
VMU-to-VMU Communications
The VMU also supports connecting to other VMU devices. This allows the the user to transfer files within the file manager of the system BIOS and exchange data within certain VMU games such as Chao Adventure.
| Pin | Function | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | CLKi | SCK1 |
| 3 | RX | SI1 |
| 4 | TX | SO1 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 10 | TX | SO0 |
| 11 | RX | SI0 |
| 13 | CLKo | SCK0 |
NOTE: During VMU-to-VMU file transfers, driven by the BIOS, RX is 1 byte delayed "echo" of TX.